2-phenylethyl isothiocyanate, beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate, PEITC, phenethyl isothiocyanate, phenethylisothiocyanate, phenylethyl isothiocyanate



| Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate | ||
| PubChem CID | 16741 | ||
| Molecular Weight | 163.24g/mol | ||
| Synonyms |
2-phenylethyl isothiocyanate, beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate, PEITC, phenethyl isothiocyanate, phenethylisothiocyanate, phenylethyl isothiocyanate |
||
| Formula | C₉H₉NS | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCN=C=S | ||
| InChI | 1S/C9H9NS/c11-8-10-7-6-9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5H,6-7H2 | ||
| InChIKey | IZJDOKYDEWTZSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CAS Number | 2257-09-2 | ||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL151649 | ||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:351346 | ||
| Drug Bank ID | DB12695 | ||
| Toxicity | Organism | Test Type | Route(Dose) |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal(165 mg/kg) | |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal(254 mg/kg) | |
| rat | LD50 | oral(322 mg/kg) | |
| Structure | 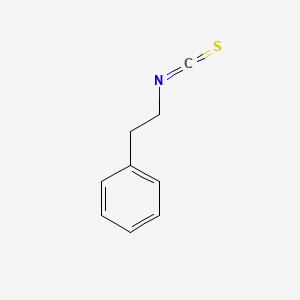
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Chineses Pinyin | DouBanCai | ||
| Use Part | Whole herb | ||
| Flavor | Sweet | ||
| Species |
>Kingdom: Viridiplantae
-->Phylum: Streptophyta
-->Class: Equisetopsida
-->Order: Brassicales
-->Family: Brassicaceae
-->Genus: Nasturtium
-->Species: Nasturtium officinale
|
||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Gefitinib | |||
| Partner Name | Gefitinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C25.Z] | Lung cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Cleavage | PARP1 | hsa142 |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | MCL1 | hsa4170 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | EIF2AK3 | hsa9451 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | EIF2S1 | hsa1965 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | DDIT3 | hsa1649 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | PMAIP1 | hsa5366 | |
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1299 | Lung large cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 |
| SK-MES-1 | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0630 | |
| In Vivo Model | NCI‐H1299 cells were subcutaneouslyinjected into the flank of mice.Mice were randomly divided into four groups (four mice pergroup) when the tumor size reached approximately 10 mm3. | |||
| Result | We explored the prospect of PEITC in improving the efficacy of targeted drug therapy and demonstrated the synergistic effects and underlined mechanisms of PEITC combined with Gefitinib in NSCLC cells treatment. This study provided useful information for developing novel therapy strategies by combination treatment of PEITC with targeted drugs. | |||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Dasatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Dasatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Blockade of cell cycle in G2/M phase | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Expression | CDK1 | hsa983 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CCNB1 | hsa891 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | KEAP1 | hsa9817 | |
| Up-regulation | Cleavage | PGAM5 | hsa192111 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | AIFM1 | hsa9131 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0327 | |
| In Vivo Model | Hepa 1-6 cells (5×10⁶ cells in 100 µL MEM) were injected subcutaneously in the right flank of 40 9–10-week-old female C57BL6 mice. | |||
| Result | PEITC showed to enhance dasatinib action in treating HCC with increased production of ROS that induced cell cycle arrest followed by mitotic catastrophe, and to induce oxeiptosis. These results highlight the role that ITCs may have in cancer therapy as a complement of clinically approved chemotherapeutic drugs | |||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Dasatinib | |||
| Partner Name | Dasatinib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C12] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Inhibition-->Angiogenesis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | PTK2 | hsa5747 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | STAT3 | hsa6774 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CDH1 | hsa999 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | CDH2 | hsa1000 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | VEGFA | hsa7422 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hep-G2 | Hepatoblastoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hepa 1-6 | Hepatocellular carcinoma of the mouse | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0327 | |
| Result | The inhibition of FAK/STAT3 signalling led to increased E-cadherin expression and reduced VEGF secretion, reducing HCC metastatic potential. Therefore, a combination of PEITC and dasatinib could be a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of HCC. | |||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Irinotecan | |||
| Partner Name | Irinotecan | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2B90.Z] | Colon cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Endoplasmic reticulum stress | |||
| Gene Regulation | Up-regulation | Expression | HSPA5 | hsa3309 |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | EIF2AK3 | hsa9451 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | EIF2S1 | hsa1965 | |
| Up-regulation | Phosphorylation | CAMK2G | hsa818 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BCL2 | hsa596 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAD | hsa572 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | BAK1 | hsa578 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CYCS | hsa54205 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | PARP1 | hsa142 | |
| Down-regulation | Expression | XIAP | hsa331 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | FAS | hsa355 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP3 | hsa836 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP8 | hsa841 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | CASP9 | hsa842 | |
| In Vitro Model | HCT 116 | Colon carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 |
| Result | PEITC potentiates IRI anticancer activity by promoting cell apoptosis in the human colon HCT 116 cells. Thus, PEITC may be a potential enhancer for IRI in humans as an anticolon cancer drug in the future. | |||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Dibenzoylmethane | |||
| Partner Name | Dibenzoylmethane | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | Prostate cancer | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 |
| Down-regulation | Expression | BIRC5 | hsa332 | |
| Down-regulation | Activity | CDH13 | hsa1012 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-3 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| DU145 | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | |
| VCaP | Prostate carcinoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2235 | |
| In Vivo Model | For a xenograft model, 2×10⁶ VCaP cells per 0.1 ml suspended in a mixture of Matrigel and RPMI 1640 medium (1 : 1) were injected subcutaneously into the back of the mice. | |||
| Result | Our results indicate that administration of DBM and PEITC in combination may be an effective strategy for inhibiting/delaying the progression of prostate cancer to androgen independence. | |||
| Pair Name | Phenethyl isothiocyanate, Cisplatin | |||
| Partner Name | Cisplatin | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | Pleural mesothelioma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->ROS generation | |||
| In Vitro Model | Meso4 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Meso11 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso13 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso34 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso47 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso56 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso96 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso76 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Meso152 | The mesothelioma cell was established from pleural fluids of patients | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Result | The combination of cisplatin with the natural compound PEITC induces a strong MPM cell death, while remaining safe for PMC, with limited emergence of cell resistance compared to drugs used alone | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phenethyl isothiocyanate synergistically induces apoptosis with Gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated degradation of Mcl-1. Mol Carcinog. 2020 Jun;59(6):590-603. doi: 10.1002/mc.23184. | Click |
| 2 | Phenethyl isothiocyanate and dasatinib combination synergistically reduces hepatocellular carcinoma growth via cell cycle arrest and oxeiptosis. Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1264032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1264032. | Click |
| 3 | Combination of Phenethyl Isothiocyanate and Dasatinib Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastatic Potential through FAK/STAT3/Cadherin Signalling and Reduction of VEGF Secretion. Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 27;15(10):2390. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15102390. | Click |
| 4 | Phenethyl isothiocyanate and irinotecan synergistically induce cell apoptosis in colon cancer HCT 116 cells in vitro. Environ Toxicol. 2024 Jan;39(1):457-469. doi: 10.1002/tox.23993. | Click |
| 5 | Phenethyl isothiocyanate in combination with dibenzoylmethane inhibits the androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Food Funct. 2018 Apr 25;9(4):2398-2408. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01983a. | Click |
| 6 | Cisplatin in combination with Phenethyl Isothiocyanate (PEITC), a potential new therapeutic strategy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 30;5(22):11641-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2604. | Click |
